Gladys Assistant 4.13 is available, and it's a big release!
We've improved the developer experience by a lot, upgraded Gladys to Node.js 18 (from 14!) and are providing a new integration for French users.
Gladys Assistant 4.13 is available, and it's a big release!
We've improved the developer experience by a lot, upgraded Gladys to Node.js 18 (from 14!) and are providing a new integration for French users.
Hi everyone!
Today, I'm happy to release Gladys Assistant 4.12 with a lots of new features.
Hi everyone!
I hope everyone spent great summer holidays 🙂
Today I'm releasing Gladys Assistant v4.10, a big new release with amazing new features, both in integrations and in the core.
Hi everyone!
Today I'm launching a new release, Gladys Assistant v4.9.
In this version, I'm bringing a new major integration to Gladys: Amazon Alexa.
It means we are now compatible with all voice assistant: Google Home and Amazon Alexa.
Hi everyone,
I'm excited to announce that we just released the compatibility with Debian 11 and Ubuntu > 20.04.
We also released a bunch of improvement that will make it more easy to install Gladys on a NAS (Synology/Unraid).
No new features were added in this release, it's a lot of long-term work & bugfixes 🙂
Hi everyone!
Today I'm happy to release a new version of Gladys, Gladys Assistant v4.8 🥳
This version is mainly focused on the calendar integration, but it also adds a lot of UX improvements in Gladys.
Hello everyone, and happy new year!
It's the tradition, every year I write an article to recap everything that has happened over the last year for Gladys Assistant.
Welcome to the 2021's version of this article 😄
Hi everyone!
This week I'm releasing a set of big features that have been asked for quite some time 🚀
Everything is available in Gladys Assistant v4.7 🥳
We now have a native way of displaying charts on the dashboard, entirely automatically and without having to setup a third-party database like InfluxDB.
To do this, Gladys is now aggregating all device data with 3 different levels of granulatity:
When displaying a chart on the dashboard, Gladys will use one of the 3 sets of aggregated data to display the chart as fast as possible.
Our goal is to stay under 100ms request time no matter the amount of data your sensor is saving.
To read more about how to setup this feature, you can read the documentation.
When releasing Zigbee2mqtt compatibility this year, we took a very prudent approach:
Each device needed to be classified manually by a developer before being able to be used in Gladys.
This approach was safer to start, because it allowed us to better integrate each device, understand a wide range of Zigbee peripherals and adapt Gladys for those devices.
But after some time, it became very repetitive to write one PR for each new Zigbee device, so we took another approach:
Auto-detecting each device!
Thanks to Alexandre Trovato #1302 Pull Request, we are now able to parse the data sent by Zigbee2mqtt to automatically map those devices to Gladys capabilities.
It means that all Zigbee2mqtt compatible devices are now compatible with Gladys, natively!
It was a common feedback, some users plug a light on a switch, and therefore they want those switches to be considered as light in Gladys.
For example, if I say "Turn on the light in the living room", it should turn on those switches as well.
It's now possible to change a switch to a light in the Tasmota integration.
Some device send a value for the temperature of their CPU.
In Gladys, we had only one "temperature" category, and the problem is that when asking for "What's the temperature in the living room?" it would answer with the temperature of the CPU of your living room computer...
Now, there is a separate "Device temperature" category to let you classify those CPU temperature clearly, without affecting the "Room temperature" feature in Gladys.
Developed in #1327.
If you installed Gladys with the official Raspberry Pi OS image, your instance will update automatically in the coming hours. It can take up to 24 hours, don't panic.
If you installed Gladys with Docker, make sure you are using Watchtower. See the documentation.
With Watchtower, Gladys will update automatically.
Thanks to everyone who contributed to this release and gave their feedback on the forum!
If you want to talk about this release, you're all welcome on the forum !
Hi !
In this tutorial I want to show you that it's possible to integrate Gladys Assistant with other cool open-source software like Node-RED.
You need to have a Gladys Assistant instance for this tutorial.
You can install Gladys Assistant on a Raspberry Pi with our pre-built Raspberry Pi OS image, or use Docker to spin up a Gladys container.
To get started, follow our documentation.
We'll use Docker to install Node-RED.
Node-RED has a Getting Started section on their website, but if you want to simply use Docker, you can run this command:
docker run -d \
--log-opt max-size=10m \
--restart=always \
--privileged \
-u root \
--network=host \
--name node_red \
-v /var/lib/node-red:/data \
nodered/node-red
A few details:
By default, Node-RED is open. We need to secure it so it's not open for everyone to use.
Node-RED admin needs to be configured in command-line.
You first need to hash your password by running the following command:
docker exec -it node_red node-red admin hash-pw
Enter your password.
It'll then display a string like:
$2b$08$6yOj6Z/ya7eDdn3eKwy4WukuyHUxiJOcZyHFiHPaCQBckKpLxUPly
This is a hashed version of the password "test"
Open the file /var/lib/node-red/settings.js by doing:
nano /var/lib/node-red/settings.js
If it doesn't work, maybe nano is not installed on your machine.
On Ubuntu/Debian, run:
sudo apt-get -y install nano
Go to the line with:
//adminAuth: {
// type: "credentials",
// users: [{
// username: "admin",
// password: "$2a$08$zZWtXTja0fB1pzD4sHCMyOCMYz2Z6dNbM6tl8sJogENOMcxWV9DN.",
// permissions: "*"
// }]
//},
Un-comment those line, and replace the password with the hashed password you generated earlier.
You should have something that looks like this:
adminAuth: {
type: "credentials",
users: [{
username: "admin",
password: "$2b$08$6yOj6Z/ya7eDdn3eKwy4WukuyHUxiJOcZyHFiHPaCQBckKpLxUPly",
permissions: "*"
}]
},
Now restart node-red with the command:
docker restart node_red
And you should be good, Node-RED should be secured!
Congrats, Node-RED should be available at IP_OF_YOUR_MACHINE:1880 !
You should see a login screen.
Here, use the the login you previously set in the settings.js file.
For me, it's:
Username: admin
Password: test
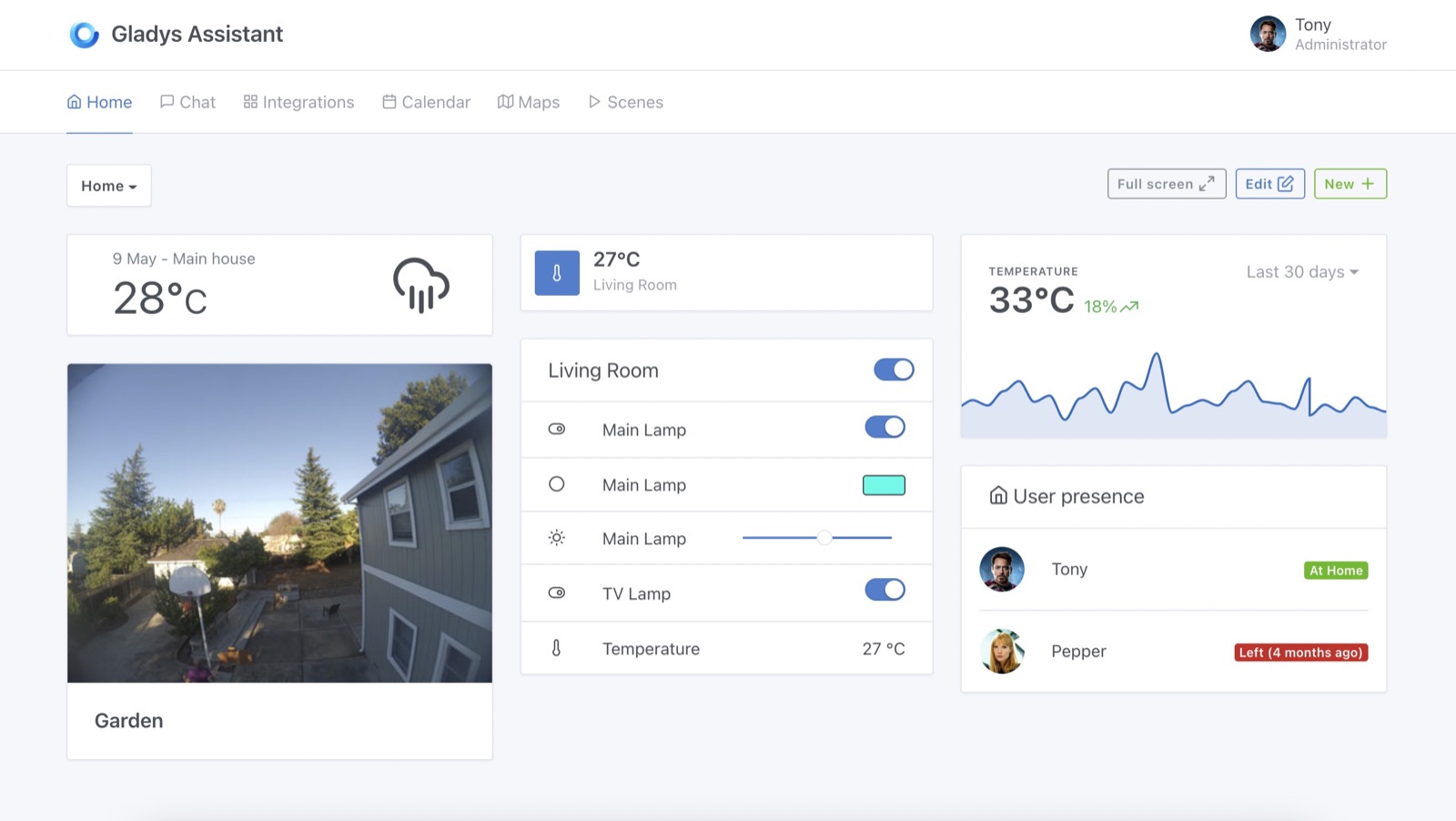
Now go to Gladys Assistant, and click on "Integrations" => "MQTT".
Go to the "Setup" tab, and click on the big blue button "Install broker in Docker" to setup a MQTT broker automatically.
You can also use a MQTT broker you already configured previously.
Back to the "Devices" tab in the MQTT integration, you can create a new device:
Copy paste the MQTT topic displayed, you'll need it for later!
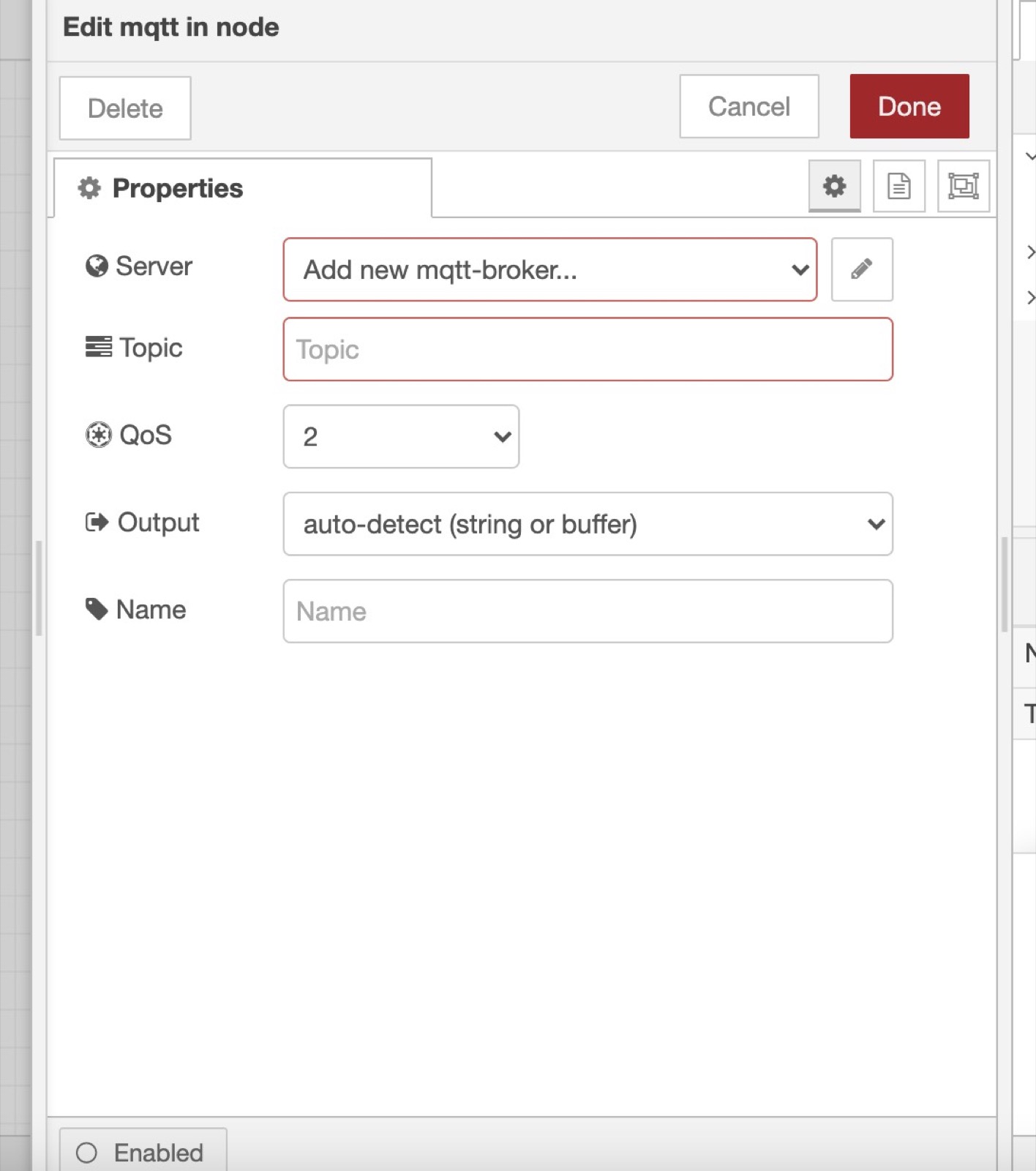
In Node-RED, you can create a "mqtt in" node to receive data from Gladys in MQTT.
You need to add the MQTT broker we just configured in Gladys by clicking on the little edit button (the pen icon next to Add new mqtt-broker):
mqtt://localhost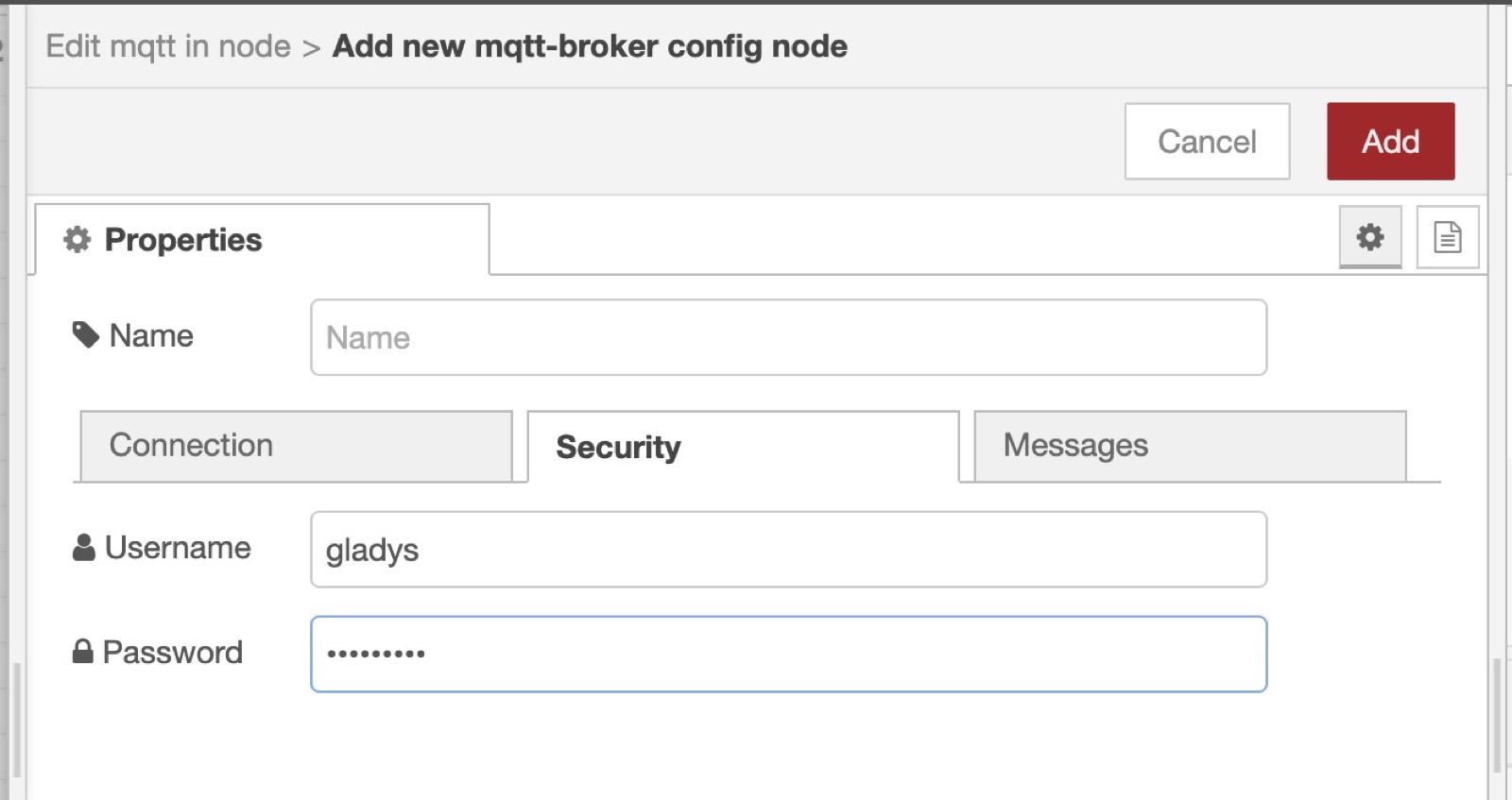
Finally, you need to paste the MQTT topic we copy pasted from Gladys when creating the device previously:
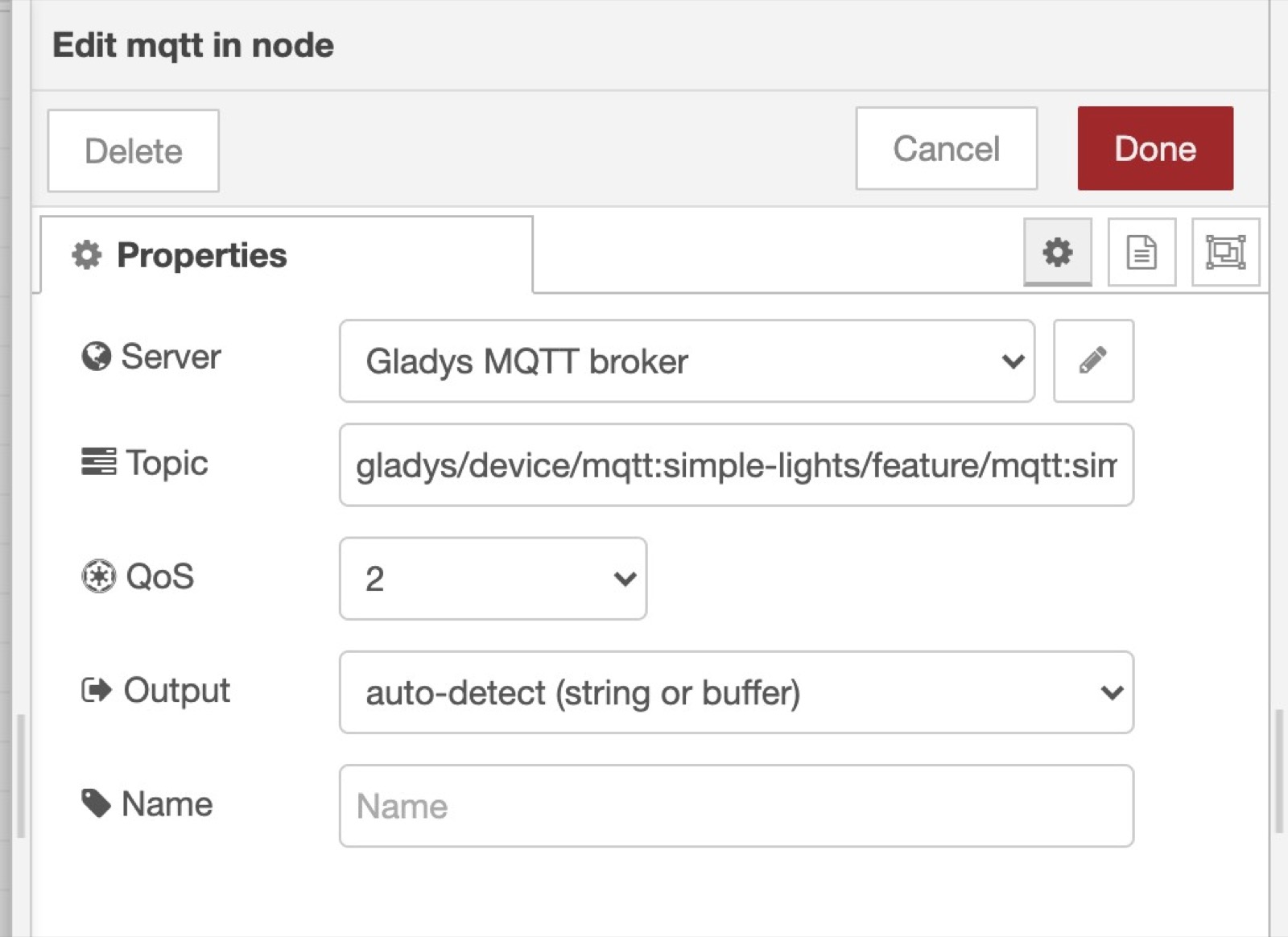
Now that this node is ready, you can connect pretty much anything to it, it'll be executed when a value is received on this MQTT topic.
You could connect a simple debug to see the data coming, or you can plug a switch case to do a different action if the data sent by Gladys is "0" (Turn Off) or "1" (Turn On).
Example:
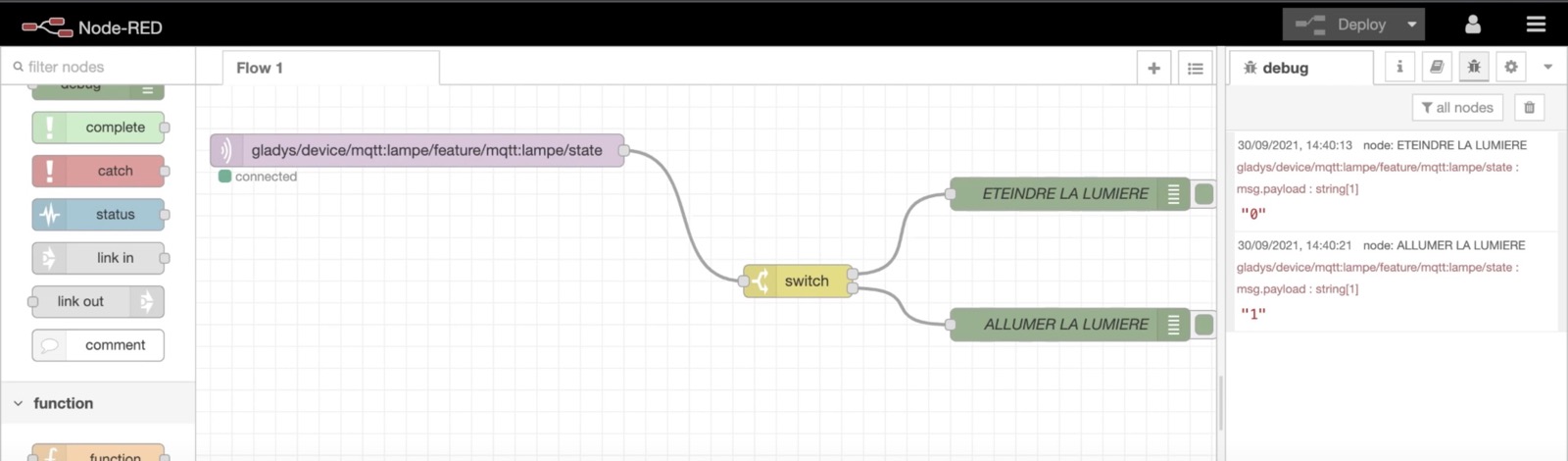
We'll do the opposite scenario in Node-RED: Sending some data from Node-RED to Gladys.
Let's imagine that I want to measure the CPU usage of my machine, and send this CPU usage every 10 seconds to Gladys.
I can create a Gladys a MQTT "CPU Usage" device:
Copy paste the MQTT topic displayed, you'll need it for later!
Add an "Inject" node in Node-RED.
Set msg.payload to a random value (Here I put 15)
Add a repeat interval at the end of the node, every 15 seconds.
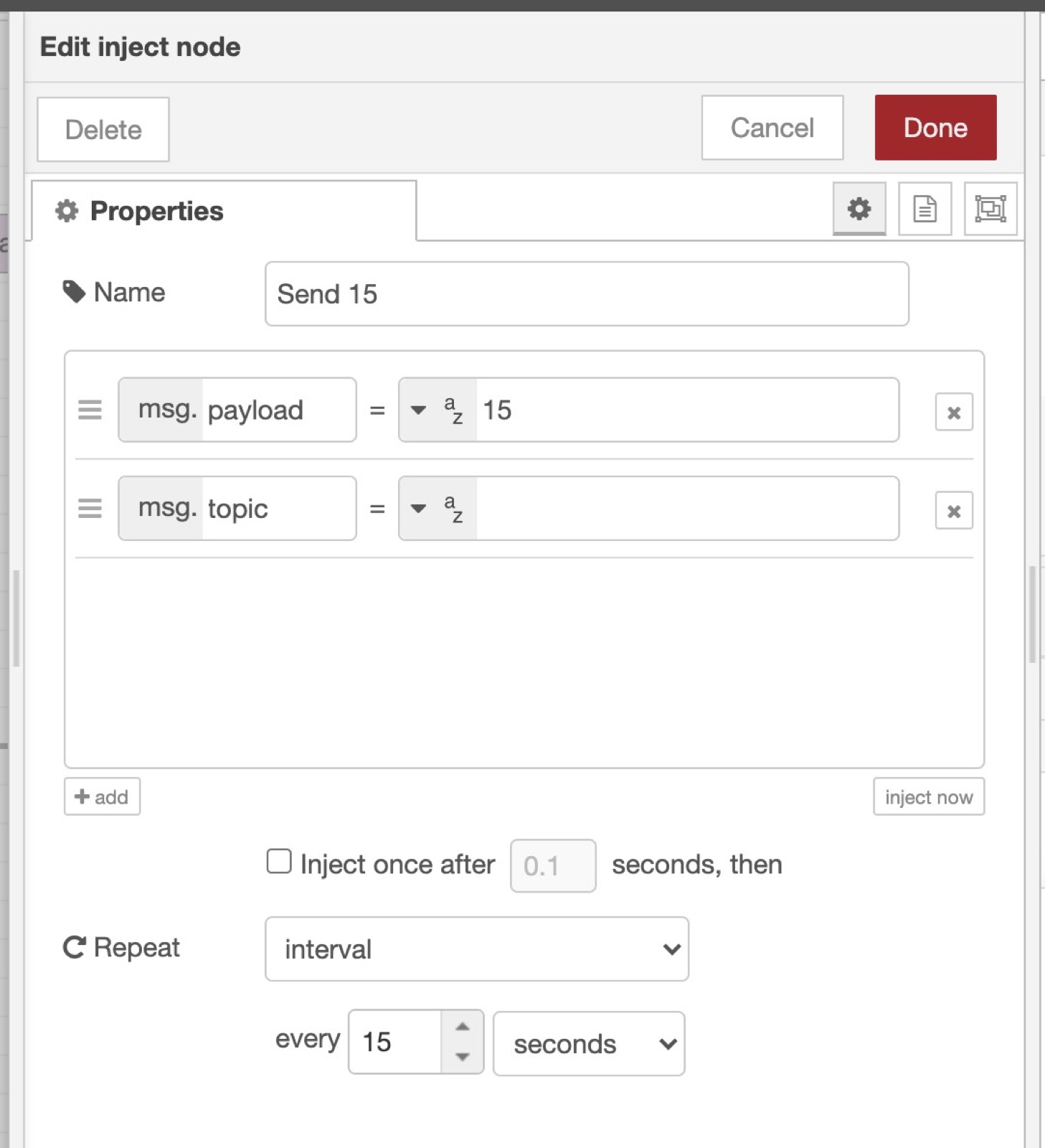
Now add a "mqtt out" node, and paste the MQTT topic we saved earlier when creating the CPU device.
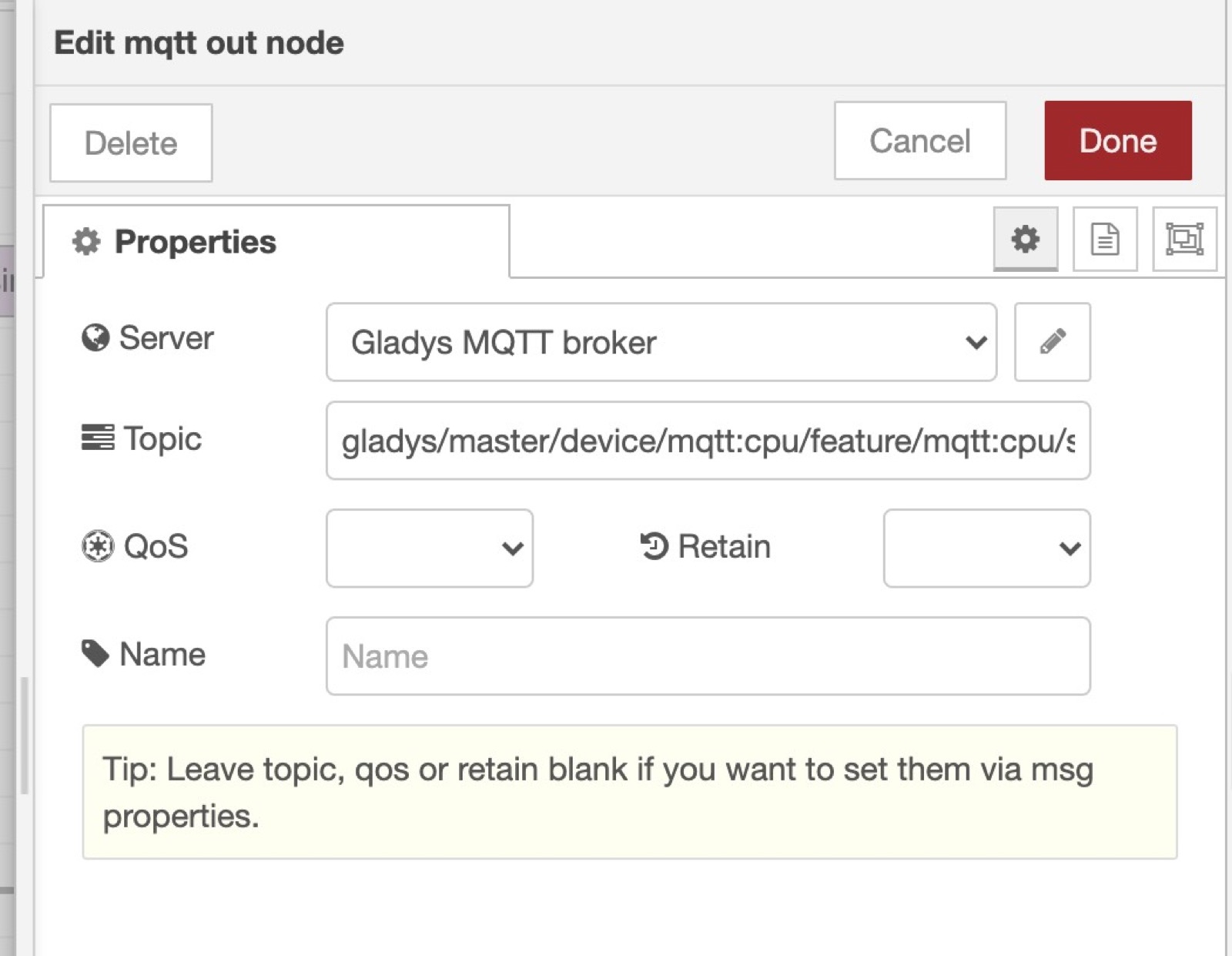
Connect the "Inject" node to the "mqtt out" node, and click "deploy".
Now you'll see that every 15 seconds, Node-RED will send the value "15" to Gladys in MQTT!
You can verify that by creating a dashboard and displaying the device we just created.
The goal of using Node-RED here is to be able to control devices that are not compatible with Gladys yet, so you might want to check their Node-RED modules to add a new compatibility in Gladys.
You can search their website
And then, in Node-RED, click on the top-right menu, then "Manage palette" to install new modules.
You can then use the installed modules in Node-RED in the left-panel.
Hi all,
Today we are releasing Gladys Assistant v4.5, a version that is bringing lots of new features to Gladys Assistant! Let me show you!
It's now possible to have multiples dashboards in Gladys Assistant.
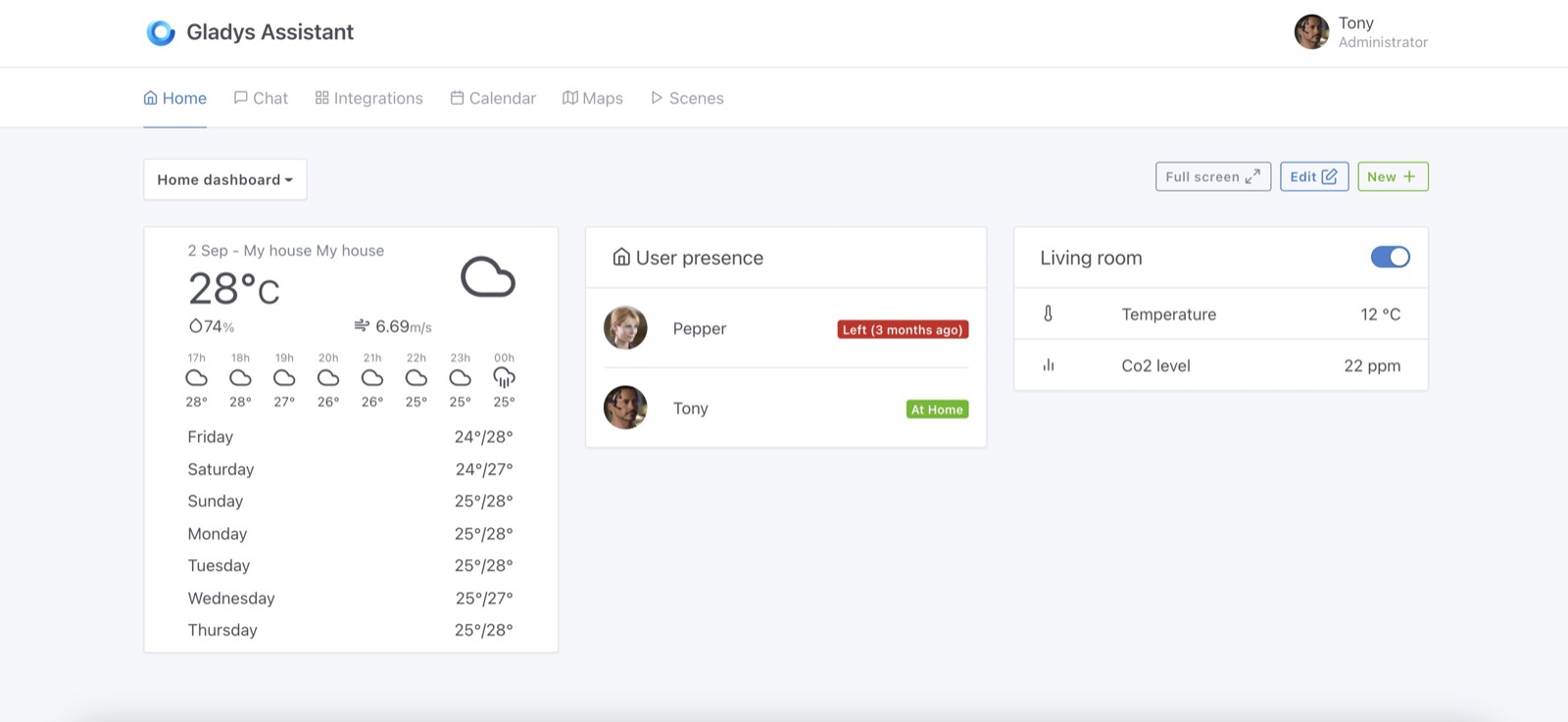
You can create several dashboards, and each of them have a unique URL, so you can add bookmarks on your browser to your favorite dashboards.
You can select the dashboard you want to display:
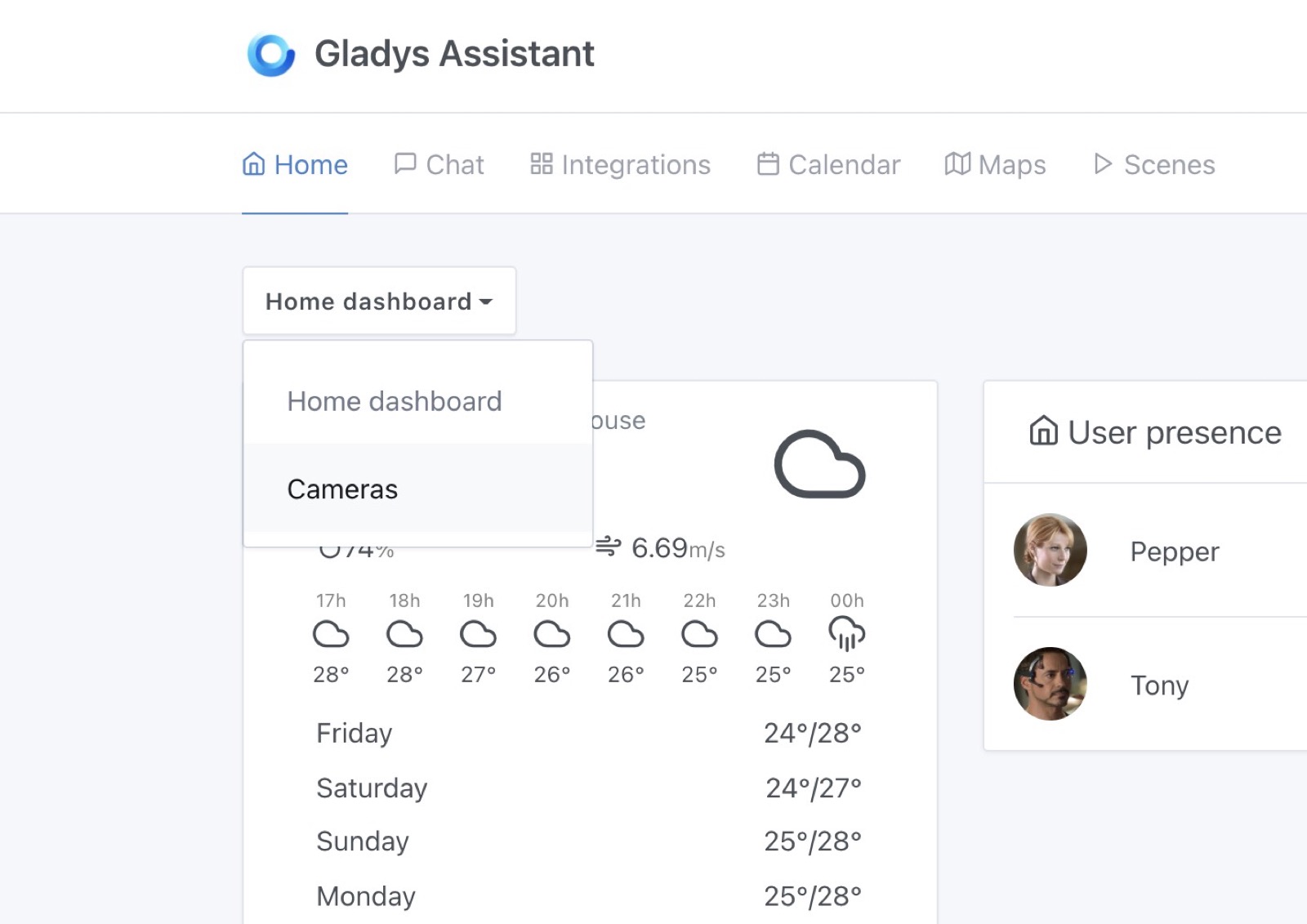
And it'll switch to another dashboard, easy!
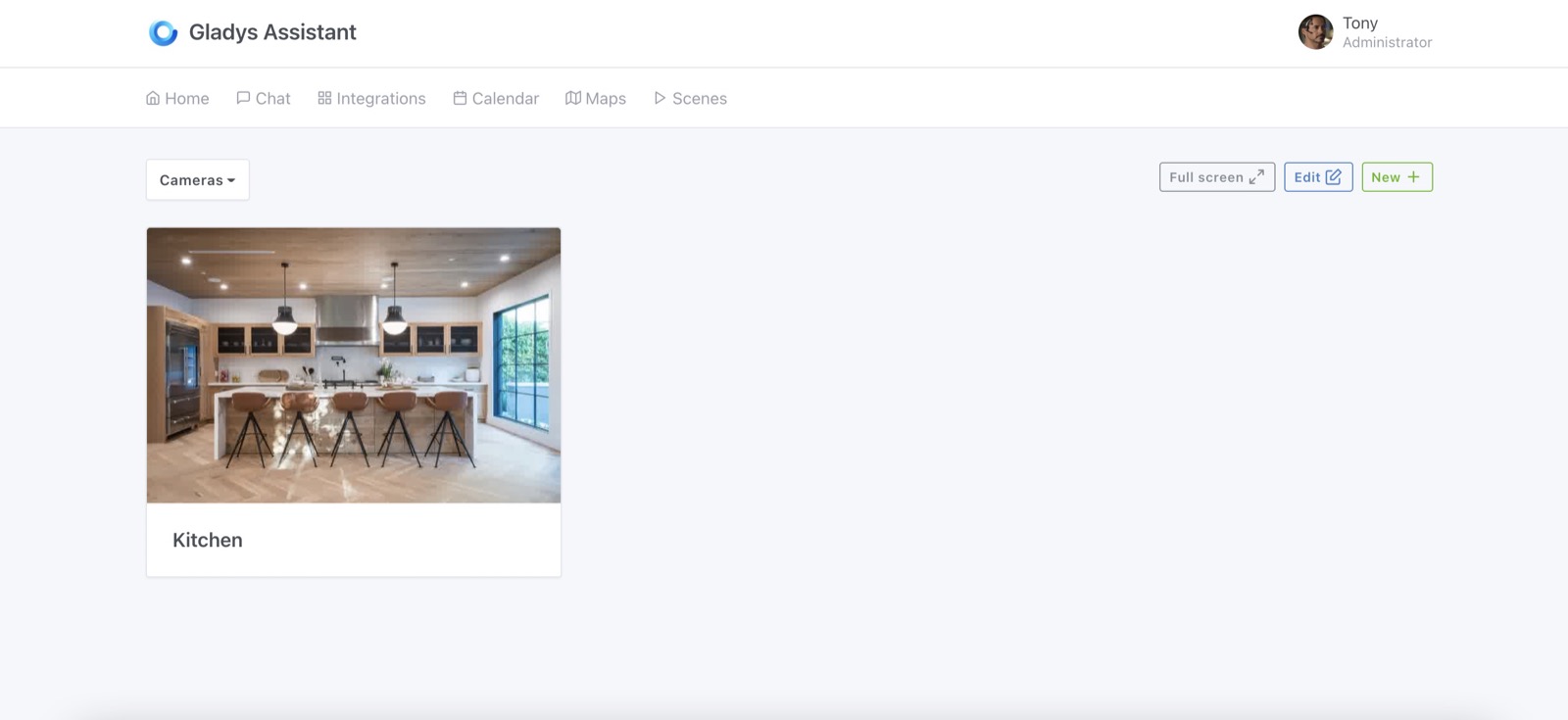
It was a highly requested feature, it's now possible to disable a scene in Gladys Assistant! Finally!
If you are prototyping a scene, going on holiday, or simply want to disable an annoying scene: you can do it now!
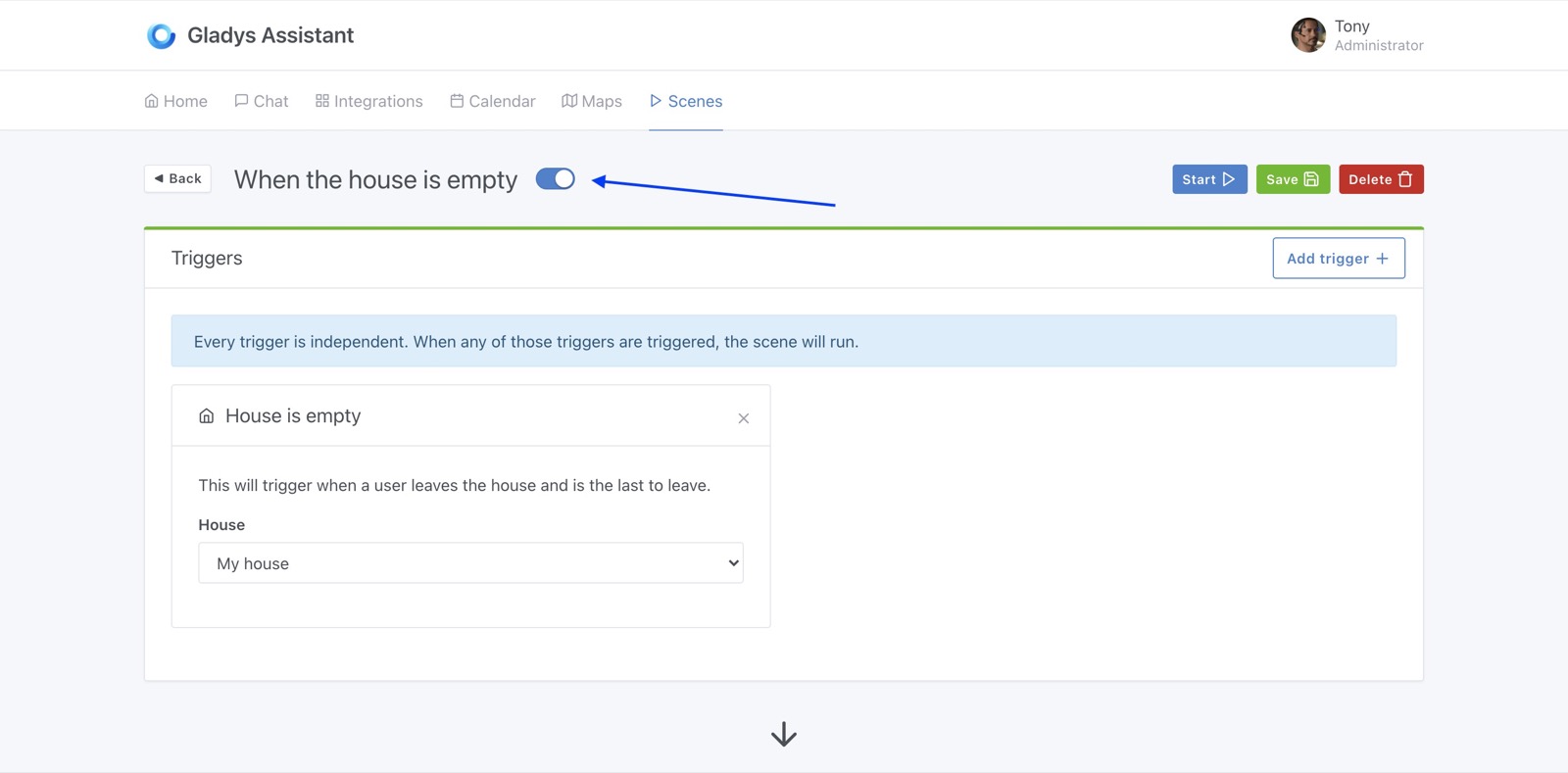
It's now possible to control any device in a scene:
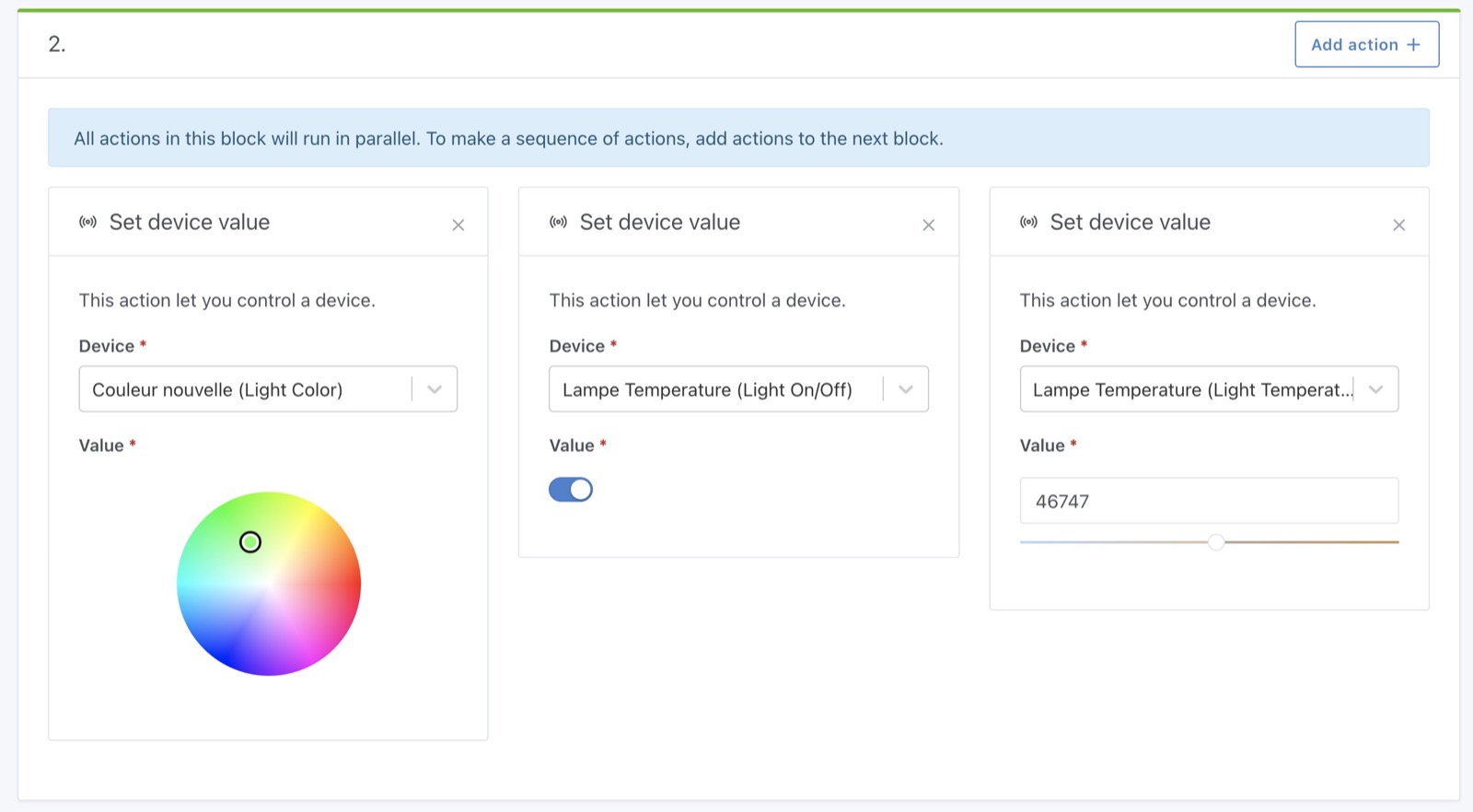
It's very powerful, and I hope you'll like it!
Small change, it's now possible to select which user to display in the "user at home" dashboard box.
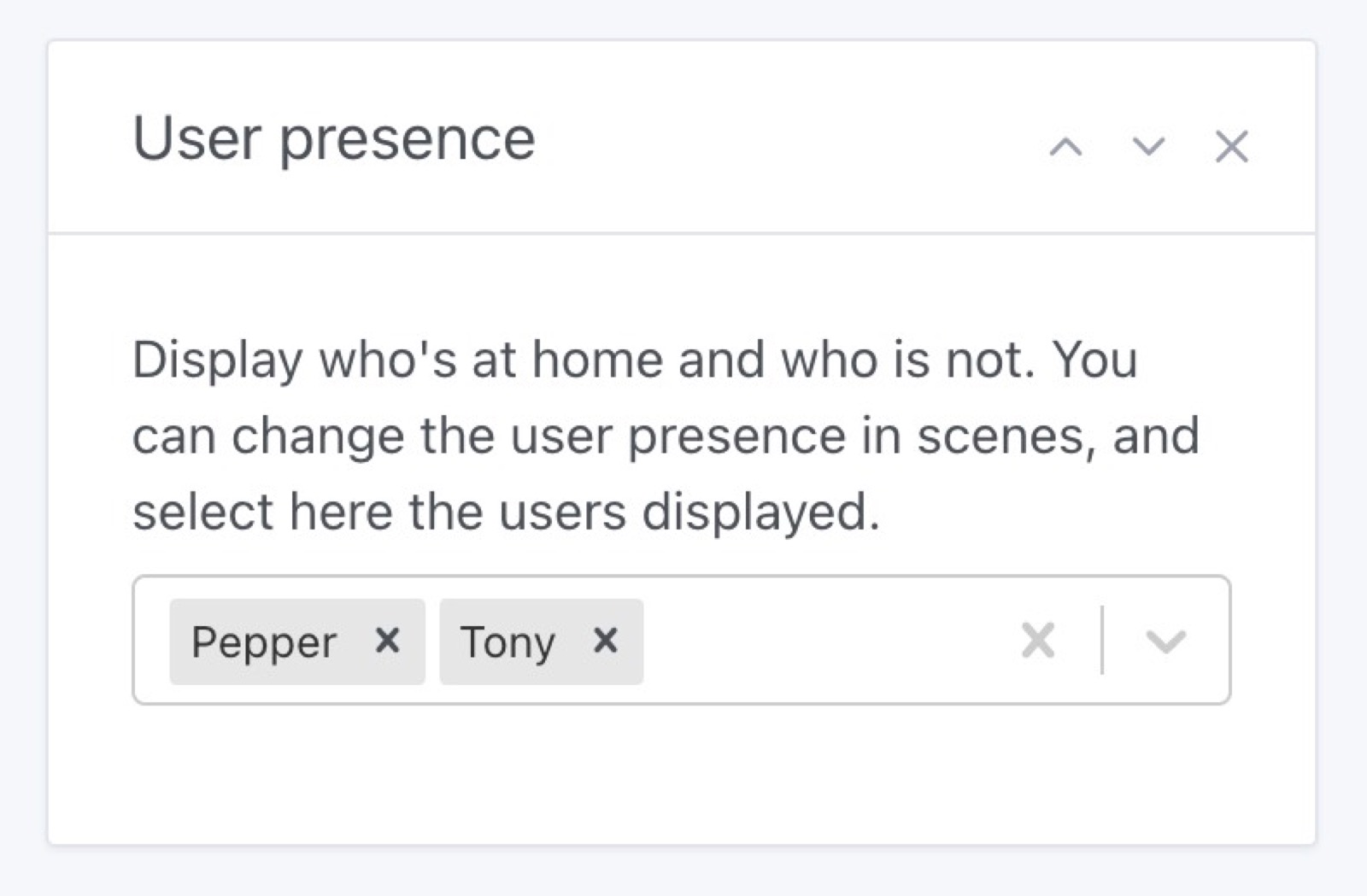
As the forum was very quiet this summer, I took the time to work on some more long-term tasks.
I migrated preact-cli (the tool we use to build Gladys frontend) to their new release 3.x. It was not easy, but definitely worth it, as it reduced by a lot the size of the javascript bundle.
I did quite some work on removing some heavy library that were not necessarely needed in the frontend, to make it lighter and faster!
I hope you'll enjoy the new speed :)
I've been working on integrating Gladys Plus with Google Home, the goal is to be able to control your devices:
Here a short demo of the integration on Twitter.
If you are interested in testing this, please send me a message on the forum!
A few new Zigbee2mqtt devices were added:
#1247#1259#1203There was a recurrent bug where Gladys was not be able to connect to the Bluetooth driver as the driver was not "ready".
This is now fixed in Gladys Assistant v4.5.
Read more on this commit: Bluetooth check state before scan + stop presence scanner #1194
If you installed Gladys with the official Raspberry Pi OS image, your instance will update automatically in the coming hours. It can take up to 24 hours, don't panic.
If you installed Gladys with Docker, make sure you are using Watchtower. See the documentation.
With Watchtower, Gladys will update automatically.
Thanks to everyone who contributed to this release and gave their feedback on the forum!
If you want to talk about this release, you're all welcom on the forum !